Neptune is a fascinating world, and not much is known about it. Perhaps, it is because Neptune is the most distant planet from the sun. Very few exploratory missions have ventured that far. Regardless, it is a planet full of wonder. It is the only planet in the solar system that is found by mathematical prediction rather than empirical observation. In this article, we discuss the nature of Neptune and more.
History
In Roman mythology, Neptune is the god of the sea. The planet is seemingly named after the sea god owing to its blue colour. After the discovery of Neptune, it was observed that its orbit was not in accordance with Newton’s law. It was, therefore, predicted that there must be another distant planet perturbing Uranus’s orbit. Neptune was first observed by Galle and Le Verrier from calculations based on the observed position of Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus.
Centuries earlier, in 1613, Galileo observed Neptune when it happened to be very near to Jupiter. But Galileo disregarded it as a star. On two successive nights, he noticed that it moved slightly with respect to a nearby star. But on subsequent nights, due to cloudy skies, it was out of his field of view. Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft that has visited Neptune. Much of what we know today comes from this single encounter.
Characteristics of Neptune
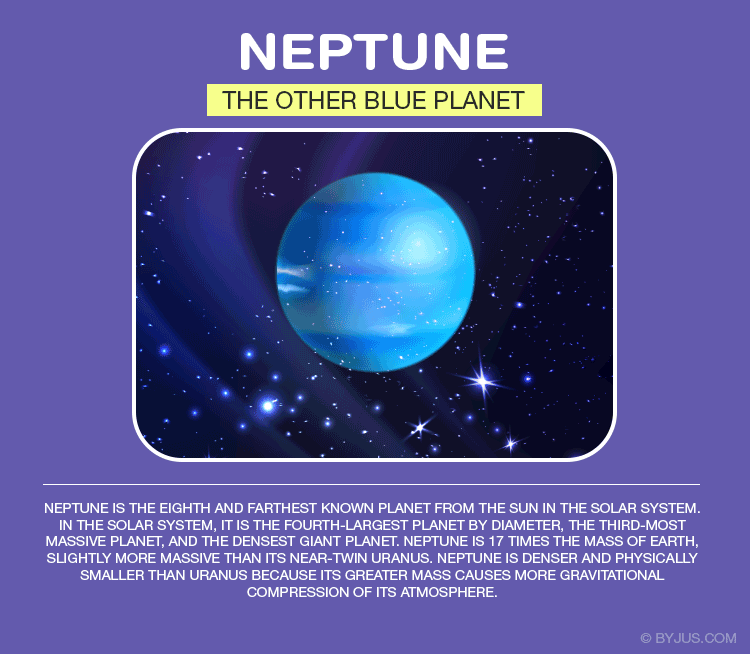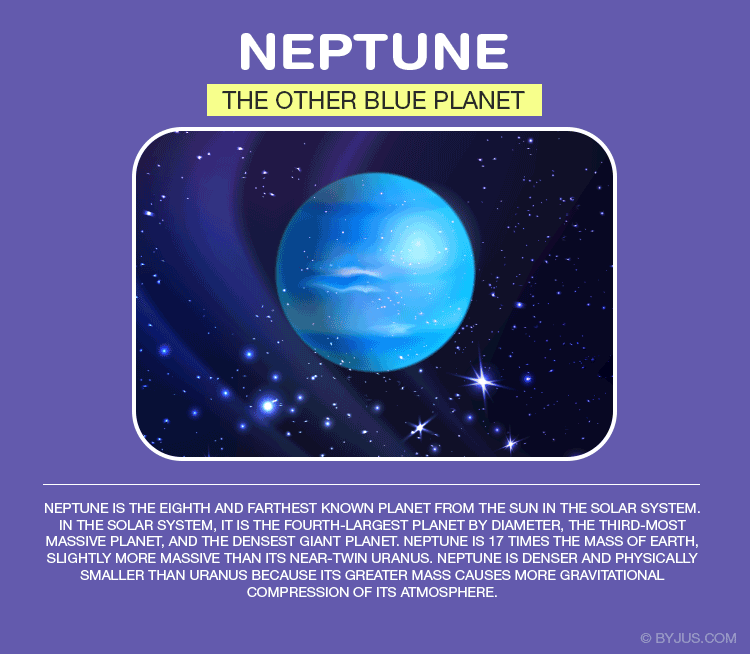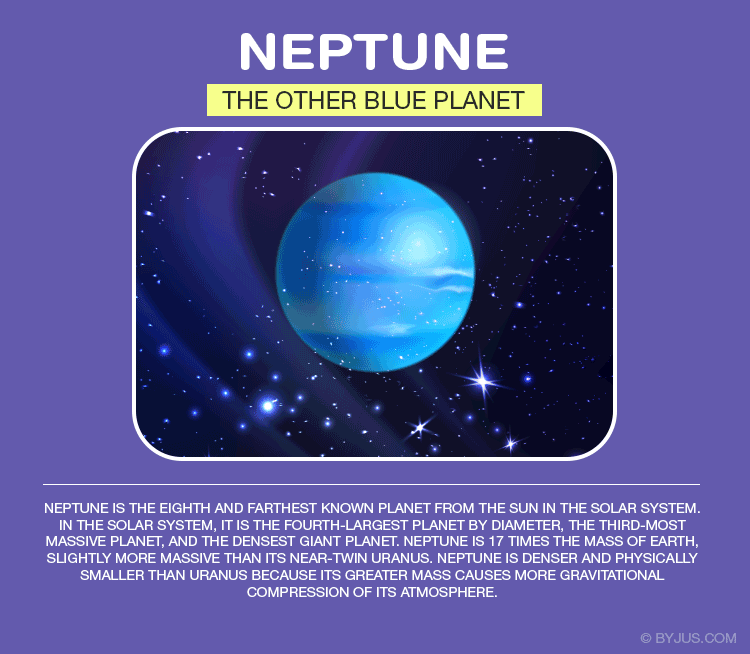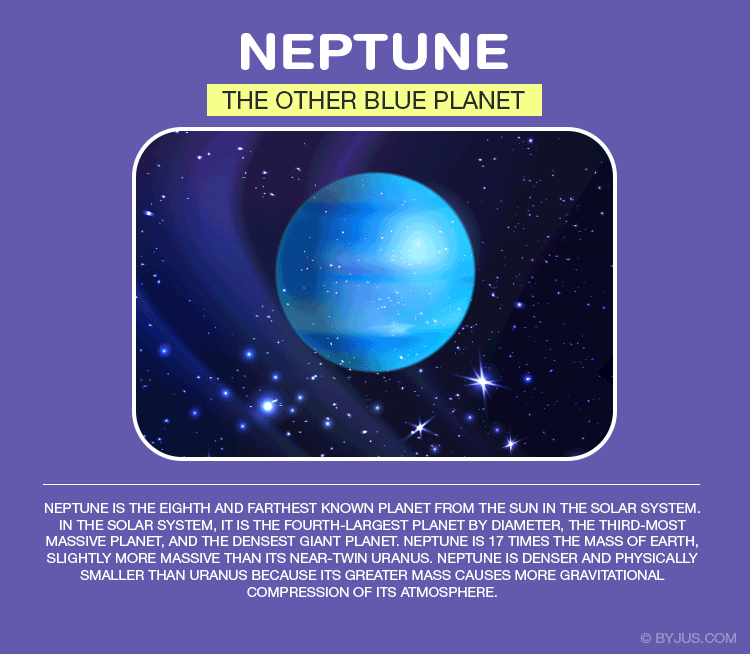
Neptune is dark, cold, and windy. It’s the last of planets in our solar system. The composition of Neptune is similar to Uranus – ice and rock with about 15% hydrogen and a little helium. Its atmosphere is made up of hydrogen, helium, and methane. Neptune’s blue colour is primarily due to the absorption of red light by methane in the atmosphere. Neptune winds are the fastest in the solar system reaching a speed of 2000 km/hr.
|
|
|
Five known rings of rock and dust encircle Neptune – all named after astronomers who helped bring light details about the windy world. Neptune also has several partial rings known as arcs.
Until another plan is crafted to visit Neptune, researchers will have to satisfy their curiosity from afar capitalizing on observations from the Hubble Space Telescope as well as telescopes that have their bases firmly planted on the ground.
0 comments :
Post a Comment